The Byford Dolphin Incident: Unraveling the Mysteries of a North Sea Disaster
The Byford Dolphin incident remains one of the most horrific accidents in the history of offshore oil exploration. It’s a case study in the dangers of saturation diving and the catastrophic consequences of human error and equipment failure. This article delves into the details of the incident, exploring the contributing factors, the immediate aftermath, and the long-term impact on safety regulations within the offshore industry. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the tragedy, honoring the lives lost and highlighting the lessons learned to prevent future occurrences.
What Was the Byford Dolphin Incident? A Detailed Examination
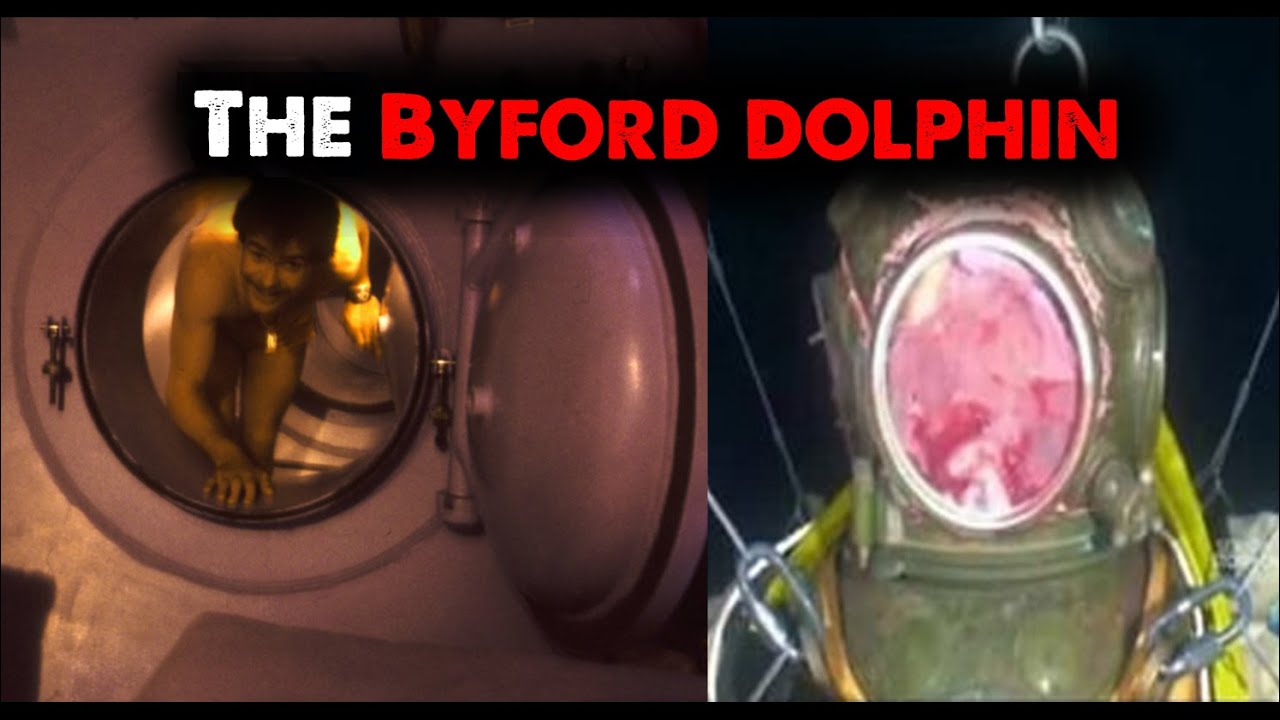
The Byford Dolphin was a semi-submersible drilling rig operating in the North Sea. On November 5, 1983, while connected to the Statfjord field, a catastrophic decompression occurred during a routine diving operation. Four divers – Edwin Arthur Coward, William Crammond, Ronald Hill, and Malcolm Saunders – lost their lives instantly. A fifth man, Lars Olay Carslen, a dive tender, also perished. The incident was not simply an accident; it was a confluence of errors and failures that exposed critical flaws in safety protocols.
The divers were part of a saturation diving team, a technique used to work at great depths for extended periods. In saturation diving, divers live in a pressurized environment, allowing them to avoid the lengthy decompression stops required for each dive. At the time of the incident, the divers were inside a diving bell connected to a complex of chambers on the rig. The decompression occurred when the diving bell was prematurely disconnected from the diving system while still under pressure. This resulted in the instantaneous depressurization of the chamber, with devastating consequences.
Understanding Saturation Diving: The Technology and the Risks
Saturation diving is a complex and inherently risky process. Divers live in a pressurized habitat for days or weeks at a time, breathing a mixture of helium and oxygen. This allows them to work efficiently at depths that would otherwise be impossible to reach. However, the process requires meticulous attention to detail and strict adherence to safety procedures.
The primary risk in saturation diving is decompression sickness, also known as “the bends.” This occurs when the nitrogen or helium dissolved in the diver’s tissues forms bubbles as the pressure decreases. These bubbles can block blood vessels, causing pain, paralysis, and even death. To prevent decompression sickness, divers must undergo a slow and controlled decompression process, allowing the gases to gradually leave their bodies.
The Byford Dolphin incident highlighted the critical importance of maintaining pressure integrity during diving operations. Any breach of pressure can have catastrophic consequences, as demonstrated by the tragic loss of life.
The Sequence of Events: A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Disaster
The events leading up to the Byford Dolphin incident were a chain of errors that ultimately resulted in the fatal decompression. Here’s a detailed reconstruction of the sequence of events:
- The divers had completed their work and were returning to the diving bell.
- The diving bell was connected to a diving system consisting of a series of chambers on the rig.
- A clamp securing the diving bell to the diving system was prematurely opened by one of the dive tenders.
- The diving bell was then detached from the diving system while still under pressure.
- This resulted in the instantaneous decompression of the chamber, killing the divers and the dive tender due to the rapid pressure change.
The precise reason for the premature opening of the clamp remains a subject of debate, but human error is widely considered to be the primary cause. The lack of clear communication, inadequate safety protocols, and a rushed work environment likely contributed to the mistake.
The Role of Human Error: Investigating the Causes of the Accident
While equipment failure may have played a minor role, the Byford Dolphin incident was primarily attributed to human error. The premature opening of the clamp was a critical mistake that could have been avoided with proper training, clear communication, and adherence to safety procedures. The investigation into the incident revealed several contributing factors:
- Lack of Communication: There was a breakdown in communication between the dive supervisor and the dive tender, leading to confusion about the status of the diving bell.
- Inadequate Training: The dive tender may not have been adequately trained on the proper procedures for disconnecting the diving bell.
- Rushed Work Environment: The pressure to complete the diving operation quickly may have contributed to the mistake.
- Poor Safety Culture: The overall safety culture on the Byford Dolphin may have been lacking, leading to a disregard for safety procedures.
These factors highlight the importance of creating a safe and supportive work environment where employees are encouraged to prioritize safety and communicate effectively.
The Immediate Aftermath: Rescue Efforts and Initial Investigations
The immediate aftermath of the Byford Dolphin incident was chaotic and traumatic. The rapid decompression caused severe injuries to the divers and the dive tender, resulting in their immediate deaths. The force of the decompression also caused significant damage to the diving system and the surrounding areas of the rig.
Rescue efforts were hampered by the dangerous conditions on the rig. The diving system was unstable, and there was a risk of further accidents. Despite these challenges, rescue workers were able to recover the bodies of the divers and the dive tender. An immediate investigation was launched to determine the cause of the incident and to prevent similar accidents from happening in the future.
The Official Investigation: Findings and Recommendations
The official investigation into the Byford Dolphin incident was conducted by the Norwegian government. The investigation concluded that the incident was caused by the premature opening of the clamp securing the diving bell to the diving system. The investigation also identified several contributing factors, including:
- Inadequate safety procedures
- Poor communication
- Insufficient training
- A rushed work environment
Based on these findings, the investigation made several recommendations to improve safety in the offshore diving industry:
- Strengthening safety regulations
- Improving training programs
- Enhancing communication protocols
- Promoting a stronger safety culture
These recommendations were implemented in the years following the incident, leading to significant improvements in safety standards in the offshore diving industry. Many of these changes are now considered standard practice.
Long-Term Impact: Changes in Safety Regulations and Industry Practices
The Byford Dolphin incident had a profound and lasting impact on safety regulations and industry practices in the offshore diving industry. The incident led to a comprehensive review of safety procedures, training programs, and equipment design.
One of the most significant changes was the introduction of stricter regulations governing saturation diving operations. These regulations included requirements for:
- More rigorous training for divers and dive tenders
- Improved communication protocols
- Enhanced safety equipment
- Regular inspections of diving systems
The incident also led to the development of new technologies designed to improve safety in saturation diving. These technologies included:
- Automated clamp systems
- Remote-controlled diving bells
- Advanced monitoring systems
These changes have significantly reduced the risk of accidents in saturation diving, making the offshore diving industry a safer place to work.
The Human Cost: Remembering the Victims of the Byford Dolphin
The Byford Dolphin incident was a tragedy that claimed the lives of five men: Edwin Arthur Coward, William Crammond, Ronald Hill, Malcolm Saunders, and Lars Olay Carslen. These men were skilled professionals who were dedicated to their work. Their deaths were a devastating loss to their families, friends, and colleagues.
It is important to remember the victims of the Byford Dolphin incident and to honor their memory by continuing to work towards a safer offshore diving industry. The lessons learned from this tragedy must never be forgotten.
Preventing Future Disasters: Lessons Learned from the Byford Dolphin
The Byford Dolphin incident serves as a stark reminder of the importance of safety in the offshore industry. The incident highlighted the dangers of saturation diving and the catastrophic consequences of human error and equipment failure. To prevent future disasters, it is essential to:
- Prioritize safety above all else
- Provide adequate training for all employees
- Foster a strong safety culture
- Maintain open communication
- Regularly inspect and maintain equipment
- Learn from past mistakes
By following these guidelines, the offshore industry can create a safer work environment and prevent future tragedies like the Byford Dolphin incident.
Modern Perspectives: How the Byford Dolphin Shapes Safety Today
The legacy of the Byford Dolphin extends far beyond the immediate aftermath of the incident. It’s a pivotal case study in risk management, human factors, and the critical need for a robust safety culture within high-hazard industries. Today, the incident is still referenced in safety training programs and serves as a benchmark for evaluating safety protocols in offshore operations. Experts frequently cite the Byford Dolphin when discussing the importance of redundancy in safety systems and the potential for seemingly minor errors to cascade into catastrophic events. The focus on clear communication, rigorous training, and proactive hazard identification stems directly from the lessons learned from this tragic event. The incident also spurred advancements in diving technology, with a greater emphasis on automation and remote operation to minimize human exposure to hazardous environments. These advancements, driven by the memory of the lives lost, represent a continuous effort to improve safety and prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
Remembering the Byford Dolphin: A Commitment to Safety
The Byford Dolphin incident was a watershed moment in the history of the offshore industry. It was a tragedy that exposed critical flaws in safety protocols and led to significant improvements in safety standards. While the memory of the incident is painful, it serves as a constant reminder of the importance of prioritizing safety above all else. By learning from the mistakes of the past, the offshore industry can create a safer work environment and prevent future tragedies. Let us honor the memory of the victims of the Byford Dolphin by recommitting ourselves to safety and ensuring that such an incident never happens again. Share your thoughts on the importance of offshore safety in the comments below.